Sciatica Pain Treatment NYC by Marc Bystock L.Ac.
"I have successfully treated thousands of sciatica patients. Even after just one to two treatments, most of my patients felt a significant reduction in their pain."
-Marc Bystock L.Ac.
Contact Marc Bystock, Leading Holistic Acupuncturist in NYC for a Free Consultation.
CONTACT MARC
VERIFY YOUR HEALTH INSURANCE
Treatments for Sciatic Pain by NYC Acupuncturist in Midtown Manhattan NY 10016
What Is Sciatica?
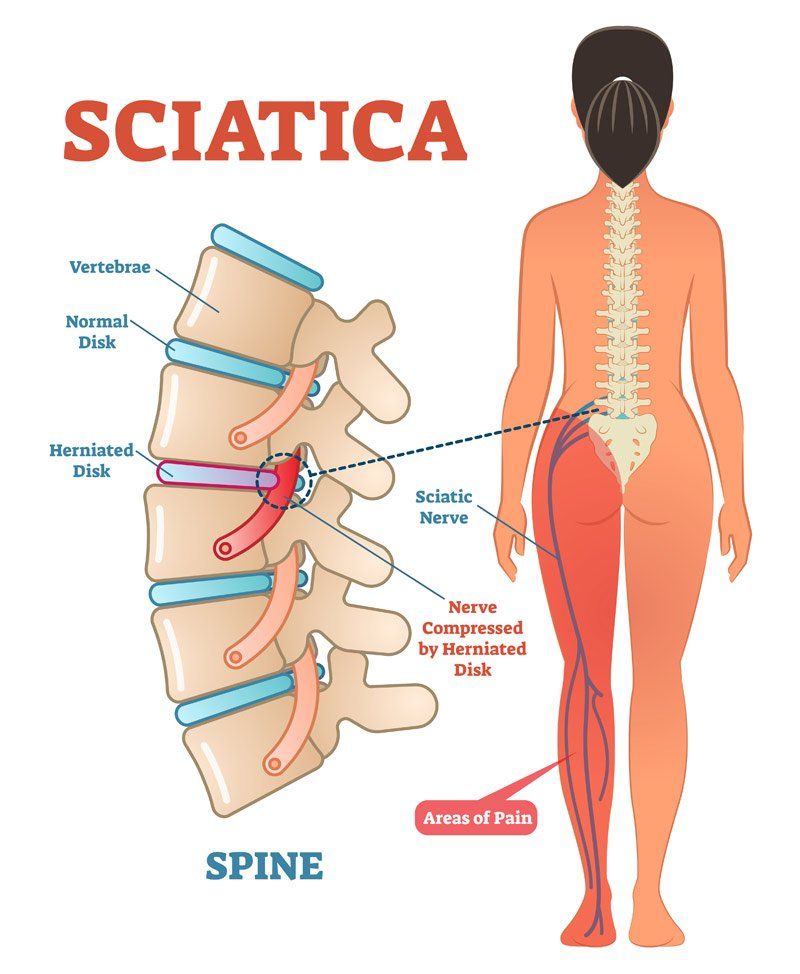
Some researchers estimate that over 50% of the general population will experience sciatica at some point in their lives. Sciatica is the pain that felt when the sciatic nerve becomes inflamed. The Sciatic nerve is the longest nerve in the human body. It emanates from between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae. It runs down from the low back, across the buttocks, past the knee and ends in the lower leg just below the knee. The level of pain caused by sciatica may vary from a small tingling pain to a severe debilitating pain where it can be difficult to ambulate.
The sciatic nerve controls many of the muscles of the lower limbs and provides a sensory response to the skin, foot, and most of the lower leg. Sciatica pain may be felt locally at the low back, or the pain may radiate traveling downward. Typically, sciatica is one-sided, but the pain may switch to the other side anytime.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica is the result of any impingement on the nerve, which causes inflammation and pain. Most often a protruding disc is at fault for placing pressure on the sciatic nerve root. Other pathology such as a bone spur or hypertonic muscles can also be enough force to cause sciatica pain to occur.
Discs are round, flat like rubbery objects. Discs lie between the bony vertebrae. They provide cushion and shock absorption to the vertebral processes. When a disc herniates from too much stress either acutely or over time, it can protrude from its donut-like center applying pressure to surrounding nerves, including the sciatic nerve causing irritation, inflammation, and pain.
The following causative factors make up the many reasons sciatica can occur:
- Lumbar herniation of the disc in over 90 % of the cases
- Direct Compression-happens when direct pressure is forced on the sciatic nerve. This may be from a herniated disc.
- Chemical inflammation- an acidic chemical like hyaluronan can leak out of the disc causing inflammation and pain
- Degenerative tissues-can break down and compress the sciatic nerve causing pain and inflammation
- Spinal stenosis- the narrowing of the channel that houses the spinal nerve. Common in older adults
- Spondylolisthesis- occurs when a vertebra slips over another vertebra, usually from a minor stress fracture, this can cause a sciatica nerve impingement
- Other causative factors-tumor, scar tissue, infection
Symptoms of Sciatica
- Leg numbness
- Tingling and a shooting pain running down the sciatic nerve
- Skin surface area may be red and warm to the touch
- Limping and difficulty ambulating
- Burning pain moving down buttocks or leg
- Low back pain
- Knee pain Pain may be worse when sitting
- Pain may extend to the foot making it difficult to move
How is Sciatica Diagnosed?
A medical history should be taken, and your physician should give a physical examination. The straight leg raise test is great to help diagnose a sciatica case. This test can determine the spinous process level, where the pathology may exist. Next, your practitioner may prescribe x-rays to search for any spinal fractures.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to look in detail at soft tissue structures for any pathology
Electromyography or nerve conductivity velocity testing (NCV) can be used to determine the rate at which the nerve impulse can travel through the sciatic nerve. A myelogram can be ordered to look for spinal pathology in a more detailed fashion. An injectable contrast dye goes into the spine while an x-ray is performed.
What is the Conventional Treatment for Sciatica?
Most often, after examination by a physician, the sciatica patient may be referred to physical therapy
This first level of treatment for sciatica is non-invasive. It will usually consist of ice and heat therapy, stretching of the nerve and surrounding tissue with exercises to strengthen the surrounding regions. In the past, bed rest was given as a therapy for sciatica. In contrast, today, patients are advised to keep moving, walking, swimming, and exercising.
The next level of therapy may consist of medication, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). Muscle relaxants such as Flexeril may be prescribed if the over the counter drugs are not effective.
A spinal injection may be performed. This is an injectable corticosteroid to drop the inflammation down, bring pain relief, and increase mobility.
Finally, there are the surgical options which may include a microdiscectomy or a laminectomy. Both procedures surgically remove either bone structure or bony fragments that may impinge into the sciatic nerve root, causing inflammation and pain.
How My Acupuncture Treatments Can Reduce Pain from Sciatica
Acupuncture is one of the pillars of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). TCM dates back over 2000 years in recorded medical history. Acupuncture is based on the principle of using very thin needles that are inserted into specific locations on the body to produce an elicited response.
Acupuncture offers a safe and effective treatment for sciatica pain relief. Its efficacy has been proven as a medical analgesic modality. Acupuncture treatments relax major muscle groups that surround the sciatica nerve area. This muscle tissue can become very tight constricting blood flow.
Next, acupuncture allows the sciatic nerve itself to relax, which lowers the inflammation and pain level.
Finally, acupuncture increases perfusion of blood flow to the region, bringing in fresh oxygen and nutrients for repair, and it increases the outflow of waste materials.
Many of the acupuncture points are also trigger points and nerve motor points. When these points are stimulated with electrical-acupuncture, the nerves can become activated, often restoring them to their original function. Also, acupuncture activates the secretion of endorphins, enkephalins, neurotransmitters, endocannabinoids, and other endogenous opioid substances to block and substantially lower pain.
Contact NYC Acupuncturist Marc Bystock L.Ac. for a Free Consultation Regarding Sciatica Treatments
I have successfully treated thousands of sciatica patients using the methods described above. The more chronically severe the patient’s symptoms may be, the more treatments the patient may require. Even after just one to two treatments, most of my patients felt a significant reduction in their pain.
If you or anyone you know suffer from sciatica pain including low back pain, knee pain and or leg pain, I want you to know that acupuncture should be considered as a first line treatment to lower the pain and inflammation and improve the quality of your life.
Please contact me
today.